Introduction: What is HIV?
HIV is a virus that can lead to AIDS, which is a condition in which the immune system is damaged and can’t fight off infections.
The virus spreads through blood and sexual fluids. It’s not spread by saliva, sweat, tears, or other body fluids. HIV can be prevented by using condoms during sex and not sharing needles with an infected person.
Some people don’t know they’re infected because there are no symptoms for 10 years or more. Others may have mild symptoms such as fever, swollen glands, a sore throat or rash that last for two weeks then go away without treatment.
What are the Symptoms of HIV Infection?
The symptoms of HIV infection are very similar to the symptoms of other illnesses. It is difficult to know if you have been infected with HIV without a blood test.
The most common symptom is fever. Other symptoms include:
– Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpits or groin
– A sore throat
– Coughing and shortness of breath
– Rash or sores on the skin
– Weight loss and night sweats
What are the Causes of HIV?
HIV is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. HIV is transmitted through bodily fluids, such as blood and semen.
HIV can be transmitted in three ways:
– Sexual contact with an infected person’s body fluids
– Exposure to infected blood
– Mother to child transmission during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding
How Does Someone Become Infected with HIV?
The way someone can become infected with HIV is through unprotected sex, shared needles, or transfusion of blood.
HIV is a virus that can be transmitted by blood, semen, vaginal fluids and breast milk. The virus can be found in these bodily fluids even when the person does not have an HIV infection.
A person gets HIV when their body comes into contact with these fluids from an infected person.
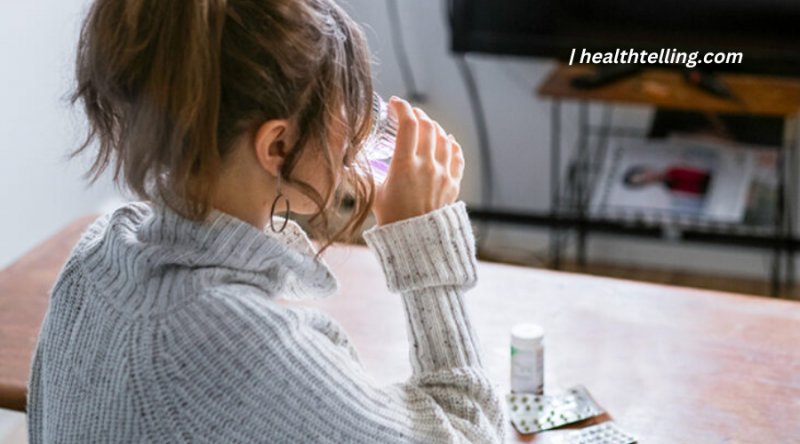
How Is HIV Treated?
HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system and can lead to AIDS. It is spread through contact with infected blood, semen, vaginal fluids or breast milk.
The most effective way to treat HIV is with antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART lowers the amount of HIV in the body and makes it less likely that HIV will be passed on to others. ART also helps people with HIV live longer, healthier lives.
There are two types of ART: 1) Antiretroviral therapy (ART) – this type of treatment uses medications (called antiretrovirals or ARVs) to stop HIV from multiplying and help keep it from spreading throughout the body. The most common type of ART is called a combination regimen because it combines three or more AR V drugs.
2) Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) – this type of treatment consists of daily use of HIV-preventive medication taken by people who don’t have HIV to stop the virus from spreading.
What Are the Different Types of Antiretroviral Drugs and Who Needs Them? (key
Antiretroviral drugs work to inhibit the HIV virus from replicating in the body. There are different types of antiretroviral drugs, each with a different use case.
There are four main types of antiretroviral drugs that work to inhibit the HIV virus from replicating in the body: nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), protease inhibitors (PIs) and integrase inhibitors.
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) stop HIV by preventing it from copying its genetic code into RNA, which is then turned into DNA. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) do not stop HIV by copying its genetic code, but by inhibiting reverse transcriptase.
3) Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) is the only HIV-1 inhibitor in a class of medications called nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs).
4) Zidovudine is an NRTI that blocks the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is necessary for the HIV virus to reproduce.