Introduction
The human body is a marvel of intricate design, where form and function are deeply interconnected. One such example is the quadratus lumborum muscle, a vital player in the orchestra of movement and stability. In this article, we will delve into the multifaceted nature of the Quadratus lumborum functions, exploring its structure, and the significant role it plays in maintaining our body’s balance and mobility.
- Understanding the Anatomy
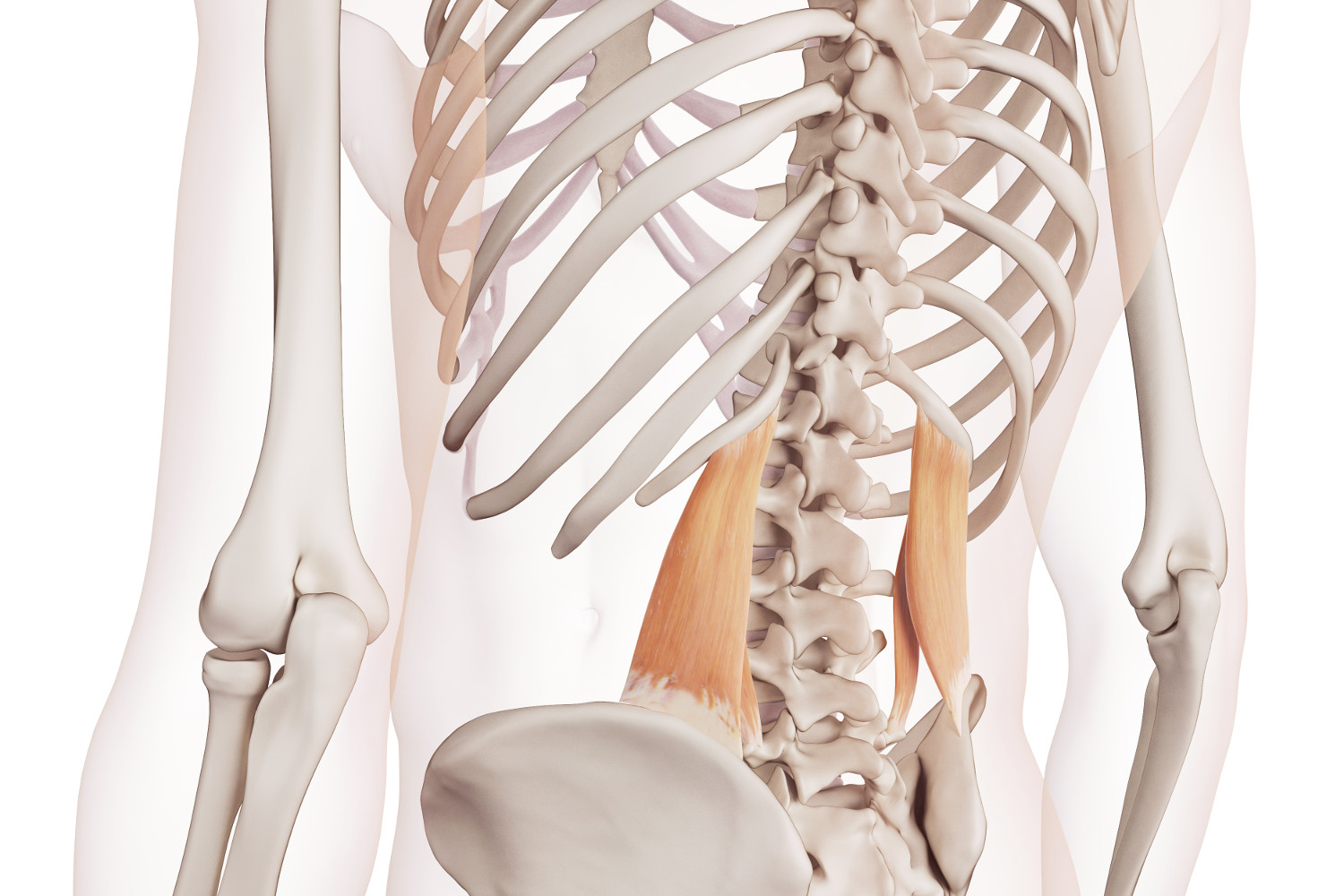
The quadratus lumborum, often abbreviated as QL, is a pair of muscles situated on each side of the lumbar spine. It originates from the iliac crest and the adjacent lumbar vertebrae, extending up to the twelfth rib. This elongated structure, resembling a quadrilateral shape, gives the muscle its name. Its complex attachments create a bridge-like form that supports various movements and postures.
Functional Roles
1. Lateral Flexion and Extension
One of the primary functions of the QL is lateral flexion, or side-bending, of the trunk. When one side’s muscle contracts, it assists in tilting the torso to the opposite side. Moreover, the QL contributes to extension, helping to arch the lower back and maintain an upright posture.
2. Stabilization
The quadratus lumborum serves as a crucial stabilizer during movement. When we lift an object or engage in activities that involve twisting, the QL works alongside other muscles to prevent excessive strain on the spine. Its stabilizing function is especially important during dynamic movements and exercises.
3. Supporting the Core
Engaging the QL effectively can lead to enhanced core stability. The muscle is part of the intricate network of core muscles responsible for maintaining a strong and balanced midsection. Proper activation of the QL can positively influence overall core strength and posture.
Common Dysfunction and Issues
1. Lower Back Pain
Dysfunction or imbalances in the QL can contribute to lower back pain. Tightness or weakness in this muscle can alter the alignment of the spine, leading to discomfort or chronic pain. Physical therapists often address these issues through targeted exercises and stretches.
2. Sciatica and Hip Imbalances
Tight QL muscles can exert pressure on nearby nerves, potentially causing sciatic pain. Additionally, imbalances in QL function can contribute to hip pain and altered gait patterns. Addressing these imbalances can alleviate discomfort and improve movement efficiency.
Exercises and Stretches for QL Health
1. Side Stretch
A simple yet effective stretch involves gently bending sideways while holding onto a stable surface. This helps lengthen and release tension in the QL, promoting flexibility and alleviating tightness.
2. Quadruped Hip Hike
Assume a quadruped position and slowly raise one hip toward the shoulder on the same side. This exercise targets the QL while also engaging the core and promoting stability.
Conclusion
The quadratus lumborum, often overlooked in discussions about core strength and stability, is a remarkable muscle that plays a crucial role in our daily movements. From lateral flexion to stabilization, its functions are diverse and essential. By understanding its anatomy and integrating targeted exercises, we can ensure a healthy and balanced musculoskeletal system. So, next time you bend, twist, or lift, remember the unsung hero that is the quadratus lumborum, tirelessly working to support your every move.